GB Syndrome
Have ever felt the absence of sensation in any part of your body for a short duration in your lifetime for a short duration? Inability to move your body intentionally? One such condition causing disability is GB syndrome or Guillain-Barre Syndrome.
Overview
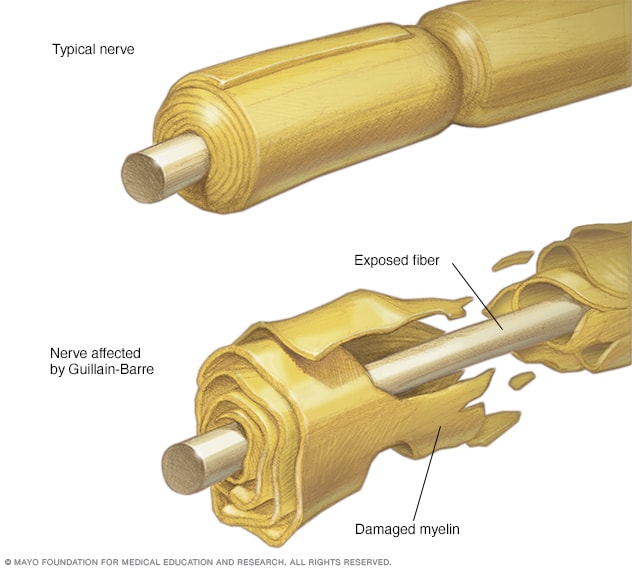
GBS is an autoimmune disease that causes neurological disorders. It can result from a viral infection, surgery, trauma or an adverse reaction to an immunisation. It is characterised by the body's immune system attacking or fighting the peripheral nervous system. Peripheral nerves outside the brain and spinal cord are affected by the inflammatory Guillain-Barré Syndrome.
It can cause muscle weakness, reflex loss, and numbness or tingling in certain areas of your body. It can result in paralysis, though this is usually only momentary. Even those with severe cases typically make a full recovery. As a matter of fact, within 6 to 12 months, 85% of individuals with GBS recover completely. It's highly unlikely to come back once you recover.
Causes
GBS typically develops after a few days or weeks of
Viral or bacterial infections - Influenza, Cytomegalovirus
Some intestinal conditions
Pneumonia
Herpes simplex virus
Infectious Mononucleosis
Dengue GBS may also be associated with the following medical conditions:
Hodgkin's disease
Systemic lupus erythematosus.
Post-surgery, it can occur at any age, with a higher prevalence in the elderly aged above 50.
Symptoms
GBS symptoms can worsen quickly. It could only take a few hours for the worst symptoms to manifest. However, a weakness that worsens over a few days is also typical. Both sides of the body are impacted by muscular weakness or loss of function (paralysis). The majority of the time, arm weakness develops from a weakness in the legs. We refer to this condition as ascending paralysis. You might require breathing assistance if the inflammation weakens the diaphragm, the big muscle that helps you breathe, and the nerves supplying those muscles.
Other typical GBS signs and symptoms include:
Absence of tendon reflexes in the limbs, Numbness or tingling (a slight loss of sensation), Loss of bladder control
Pain or tenderness in the muscles
Difficulty in moving the limbs, Incoherent gait (unable to walk without assistance)
Low or inadequate blood pressure
Blurred and double vision, clumsiness, and trip hazards
Having trouble using the facial muscles
Feeling the palpitations in your heartbeat
Ayurvedic View
Vata vyadhi- it is vata dosha predominant disease, where this aggravated vata enters sira (blood vessels, nerves) and snayu (tendons, ligaments), dries these by vata dosha ruksha (drying quality) and causes sandhi vishlesha (looseness of affected joint), suptatha (numbness), pain, weakness, etc. This is GB syndrome. The Ayurveda way of approach is to correct agni (metabolism), bring dosha back to prakruta awastha (balanced state), to rehabilitate the affected area by ayurvedic panchakarma treatment and treatment done locally so as to stimulate the nerves' lost function.
GB Syndrome
Treatment for
DISCLAIMER: Listed treatment details are only for information purposes. Treatments and duration may vary depending on numerous factors. Treatments for your condition may not be limited to this list.






















