Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
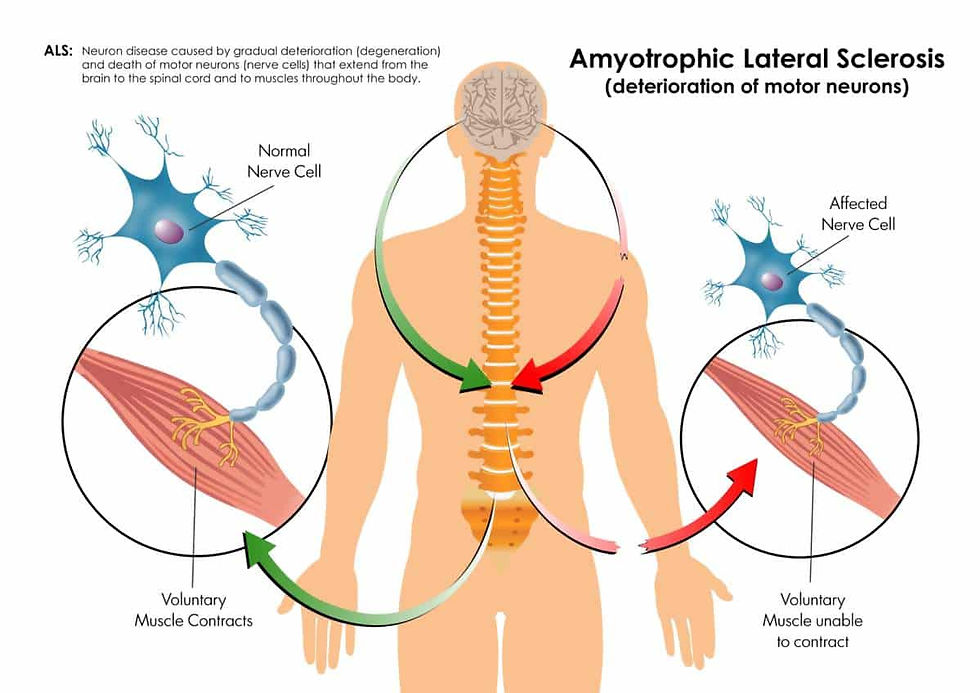
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis also known as ALS is a neurodegenerative illness that gradually damages brain and spinal cord nerve cells.
Overview
The word "amyotrophic" is derived from Greek. "A" indicates no. The word "myo" means muscle. The word "trophic" means "nourishing." Thus, the term "amyotrophic" refers to "no muscle nourishment " and a muscle that is starved of nutrients "atrophies" or deteriorates. The term "lateral" describes the regions of the spinal cord that contain some of the nerve cells that communicate with and regulate the muscles. This degeneration causes scarring or hardening ("sclerosis") in the affected area.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis affects nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord. Muscle control is lost in ALS patients. The illness worsens with time. Since baseball player Lou Gehrig was diagnosed with ALS, the illness is frequently referred to as Lou Gehrig's disease. It primarily affects motor neurons. It’s a neurological condition that causes physical function to be impaired and muscles to wither. It causes both the malfunction of the muscles that these nerve cells supply and the degeneration of nerve cells themselves.
Causes
The exact cause of ALS is unknown, but some factors may increase the risk, such as
Genetic mutations
Immune system problems
Oxidative stress and environmental toxins.
About 10% of ALS cases are inherited, and more than 12 genes linked to the disease have been discovered. The most common one is SOD1, which affects protein function.
Symptoms
The onset of ALS symptoms usually occurs after the age of 50. Early-stage symptoms of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis include:
Twitches in the tongue, arm, leg or shoulder muscles and cramping with a progressive loss of muscle strength and coordination. This loss of strength makes it difficult for people with ALS to perform routine tasks such as climbing stairs, getting out of a chair, or swallowing. Weakness can initially impair breathing or swallowing as well as the arms or legs.
More muscle groups experience issues as the illness worsens. Since the disease can affect all skeletal
Muscle weakness can eventually lead to
Breathing difficulties,
Swallowing difficulties,
Difficulty walking,
Speech changes,
Anxiety,
Depression
Difficulty maintaining nutrition.
Not every person with this disease will experience every symptom, and it can be challenging to predict which symptoms each person may develop because each person with the disease has a unique appearance. The senses (sight, smell, taste, hearing, and touch) are unaffected by ALS. While a small percentage of people experience dementia, which impairs speech and thought, most people can think normally.
Ayurvedic View
Snayu gata vata - Due to the following of nidana (causes ) that aggravate vata dosha, this vikruta prakupita (aggravated) vyana vata dosha takes sthana samshraya (settles) in snayu (which is connected to motor movements), which causes twitching pain and diseases affecting ekanga (part),sarvanga (whole body), degenerative disease, which can cause difficulty in good functioning and movement of the body. This disease is ALS. The Ayurveda way of approach is to bring dosha back to prakruta awastha (balance state) in guna (qualitatively),sthana (place ), karma (functional aspect), and help in the rehabilitation of the affected part by Ayurvedic panchakarma treatment.
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
Treatment for
DISCLAIMER: Listed treatment details are only for information purposes. Treatments and duration may vary depending on numerous factors. Treatments for your condition may not be limited to this list.






















